This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2017) |

Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an audio source privately, in contrast to a loudspeaker, which emits sound into the open air for anyone nearby to hear. Headphones are also known as earphones[1] or, colloquially, cans.[2] Circumaural (around the ear) and supra-aural (over the ear) headphones use a band over the top of the head to hold the drivers in place. Another type, known as earbuds or earpieces,[1] consists of individual units that plug into the user's ear canal; within that category have been developed cordless air buds using wireless technology. A third type are bone conduction headphones, which typically wrap around the back of the head and rest in front of the ear canal, leaving the ear canal open. In the context of telecommunication, a headset is a combination of a headphone and microphone.
Headphones connect to a signal source such as an audio amplifier, radio, CD player, portable media player, mobile phone, video game console, or electronic musical instrument, either directly using a cord, or using wireless technology such as Bluetooth, DECT or FM radio. The first headphones were developed in the late 19th century for use by switchboard operators, to keep their hands free. Initially, the audio quality was mediocre and a step forward was the invention of high fidelity headphones.[3][4]
Headphones exhibit a range of different audio reproduction quality capabilities. Headsets designed for telephone use typically cannot reproduce sound with the high fidelity of expensive units designed for music listening by audiophiles. Headphones that use cables typically have either a 1⁄4 inch (6.4 mm) or 1⁄8 inch (3.2 mm) phone jack for plugging the headphones into the audio source. Some headphones are wireless, using Bluetooth connectivity to receive the audio signal by radio waves from source devices like cellphones and digital players.[5] As a result of the Walkman effect, beginning in the 1980s, headphones started to be used in public places such as sidewalks, grocery stores, and public transit.[6] Headphones are also used by people in various professional contexts, such as audio engineers mixing sound for live concerts or sound recordings and DJs, who use headphones to cue up the next song without the audience hearing, aircraft pilots and call center employees. The latter two types of employees use headphones with an integrated microphone.
History
[edit]
Headphones grew out of the need to free up a person's hands when operating a telephone.[7] By the 1880s, soon after the invention of the telephone, telephone switchboard operators began to use head apparatuses to mount the telephone receiver.[8] The receiver was mounted on the head by a clamp which held it next to the ear.[9] The head mount freed the switchboard operator's hands, so that they could easily connect the wires of the telephone callers and receivers.[10] The head-mounted telephone receiver in the singular form was called a headphone.[11][12] These head-mounted phone receivers, unlike modern headphones, only had one earpiece.[13]
By the 1890s a listening device with two earpieces was developed by the British company Electrophone. The device created a listening system through the phone lines that allowed the customer to connect into live feeds of performances at theaters and opera houses across London. Subscribers to the service could listen to the performance through a pair of massive earphones that connected below the chin and were held by a long rod.[14]
French engineer Ernest Mercadier in 1891 patented a set of in-ear headphones.[15][14] The German company Siemens Brothers at this time was also selling headpieces for telephone operators which had two earpieces, although placed outside the ear. The Siemens Brothers headpieces looked similar to modern headphones. The majority of headgear used by telephone operators continued to have only one earpiece.[16]

Headphones appeared in the emerging field of wireless telegraphy, which was the beginning stage of radio broadcasting. Some early wireless telegraph developers chose to use the telephone receiver's speaker as the detector for the electrical signal of the wireless receiving circuit.[17] By 1902 wireless telegraph innovators, such as Lee de Forest, were using two jointly head-mounted telephone receivers to hear the signal of the receiving circuit.[18] The two head-mounted telephone receivers were called in the singular form head telephones.[17] By 1908 the headpiece began to be written simply as head phones,[19] and a year later the compound word headphones began to be used.[20]

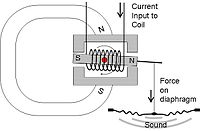
One of the earliest companies to make headphones for wireless operators was the Holtzer-Cabot Company in 1909.[21] They were also makers of head receivers for telephone operators and normal telephone receivers for the home.[21] Another early manufacturer of headphones was Nathaniel Baldwin.[22] He was the first major supplier of headsets to the U.S. Navy.[23] In 1910, motivated by his inability to hear sermons during Sunday service, he invented a prototype telephone headset.[24] He offered it for testing to the navy, which promptly ordered 100 of them. Wireless Specialty Apparatus Co., in partnership with Baldwin Radio Company, set up a manufacturing facility in Utah to fulfill orders.[25] These early headphones used moving iron drivers,[26] with either single-ended or balanced armatures. The common single-ended type used voice coils wound around the poles of a permanent magnet, which were positioned close to a flexible steel diaphragm. The audio current through the coils varied the magnetic field of the magnet, exerting a varying force on the diaphragm, causing it to vibrate, creating sound waves. The requirement for high sensitivity meant that no damping was used, so the frequency response of the diaphragm had large peaks due to resonance, resulting in poor sound quality. These early models lacked padding, and were often uncomfortable to wear for long periods. Their impedance varied; headphones used in telegraph and telephone work had an impedance of 75 ohms. Those used with early wireless radio had more turns of finer wire to increase sensitivity. Impedances of 1,000 to 2,000 ohms was common, which suited both crystal sets and triode receivers. Some very sensitive headphones, such as those manufactured by Brandes around 1919, were commonly used for early radio work.
In 1958, John C. Koss, an audiophile and jazz musician from Milwaukee, produced the first stereo headphones.[27][26]
Smaller earbud type earpieces, which plugged into the user's ear canal, were first developed for hearing aids. They became widely used with transistor radios, which commercially appeared in 1954 with the introduction of the Regency TR-1. The most popular audio device in history, the transistor radio changed listening habits, allowing people to listen to the radio anywhere. The earbud uses either a moving iron driver or a piezoelectric crystal to produce sound. The 3.5 mm radio and phone connector, which is the most commonly used in portable applications today, has been used at least since the Sony EFM-117J transistor radio, which was released in 1964.[28][29] Its popularity was reinforced by its use on the Walkman portable tape player in 1979.
Applications
[edit]Headphones may be used with stationary CD and DVD players, home theater, personal computers, or portable devices (e.g., digital audio player/MP3 player, mobile phone), as long as these devices are equipped with a headphone jack. Cordless headphones are not connected to their source by a cable. Instead, they receive a radio or infrared signal encoded using a radio or infrared transmission link, such as FM, Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. These are battery-powered receiver systems, of which the headphone is only a component. Cordless headphones are used with events such as a Silent disco or Silent Gig.

In the professional audio sector, headphones are used in live situations by disc jockeys with a DJ mixer, and sound engineers for monitoring signal sources. In radio studios, DJs use a pair of headphones when talking to the microphone while the speakers are turned off to eliminate acoustic feedback while monitoring their own voice. In studio recordings, musicians and singers use headphones to play or sing along to a backing track or band. In military applications, audio signals of many varieties are monitored using headphones.
Wired headphones are attached to an audio source by a cable. The most common connectors are 6.35 mm (1⁄4 inch) and 3.5 mm phone connectors. The larger 6.35 mm connector is more common on fixed location home or professional equipment. The 3.5 mm connector remains the most widely used connector for portable application today. Adapters are available for converting between 6.35 mm and 3.5 mm devices.

As active component, wireless headphones tend to be costlier due to the necessity for internal hardware such as a battery, a charging controller, a speaker driver, and a wireless transceiver, whereas wired headphones are a passive component, outsourcing speaker driving to the audio source.
Some headphone cords are equipped with a serial potentiometer for volume control.
Wired headphones may be equipped with a non-detachable cable or a detachable auxiliary male-to-male plug, as well as some with two ports to allow connecting another wired headphone in a parallel circuit, which splits the audio signal to share with another participant, but can also be used to hear audio from two inputs simultaneously. An external audio splitter can retrofit this ability.[30]
Applications for audiometric testing
[edit]Various types of specially designed headphones or earphones are also used to evaluate the status of the auditory system in the field of audiology for establishing hearing thresholds, medically diagnosing hearing loss, identifying other hearing related disease, and monitoring hearing status in occupational hearing conservation programs.[31] Specific models of headphones have been adopted as the standard due to the ease of calibration and ability to compare results between testing facilities.[32]
Supra-aural style headphones are historically the most commonly used in audiology as they are the easiest to calibrate and were considered the standard for many years. Commonly used models are the Telephonics Dynamic Headphone (TDH) 39, TDH-49, and TDH-50. In-the-ear or insert style earphones are used more commonly today as they provide higher levels of interaural attenuation, introduce less variability when testing 6,000 and 8,000 Hz, and avoid testing issues resulting from collapsed ear canals. A commonly used model of insert earphone is the Etymotic Research ER-3A. Circum-aural earphones are also used to establish hearing thresholds in the extended high frequency range (8,000 Hz to 20,000 kHz). Along with Etymotic Research ER-2A insert earphones, the Sennheiser HDA300 and Koss HV/1A circum-aural earphones are the only models that have reference equivalent threshold sound pressure level values for the extended high frequency range as described by ANSI standards.[33][32][34]
Audiometers and headphones must be calibrated together. During the calibration process, the output signal from the audiometer to the headphones is measured with a sound level meter to ensure that the signal is accurate to the reading on the audiometer for sound pressure level and frequency. Calibration is done with the earphones in an acoustic coupler that is intended to mimic the transfer function of the outer ear. Because specific headphones are used in the initial audiometer calibration process, they cannot be replaced with any other set of headphones, even from the same make and model.[32]
Electrical characteristics
[edit]Electrical characteristics of dynamic loudspeakers may be readily applied to headphones, because most headphones are small dynamic loudspeakers.
Impedance
[edit]Headphones are available with high or low impedance (typically measured at 1 kHz). Low-impedance headphones are in the range 16 to 32 ohms and high-impedance headphones are about 100-600 ohms. As the impedance of a pair of headphones increases, more voltage (at a given current) is required to drive it, and the loudness of the headphones for a given voltage decreases. In recent years, impedance of newer headphones has generally decreased to accommodate lower voltages available on battery powered CMOS-based portable electronics. This has resulted in headphones that can be more efficiently driven by battery-powered electronics. Consequently, newer amplifiers are based on designs with relatively low output impedance.
The impedance of headphones is of concern because of the output limitations of amplifiers. A modern pair of headphones is driven by an amplifier, with lower impedance headphones presenting a larger load. Amplifiers are not ideal; they also have some output impedance that limits the amount of power they can provide. To ensure an even frequency response, adequate damping factor, and undistorted sound, an amplifier should have an output impedance less than 1/8 that of the headphones it is driving (and ideally, as low as possible). If output impedance is large compared to the impedance of the headphones, significantly higher distortion is present.[35] Therefore, lower impedance headphones tend to be louder and more efficient, but also demand a more capable amplifier. Higher impedance headphones are more tolerant of amplifier limitations, but produce less volume for a given output level.
Historically, many headphones had relatively high impedance, often over 500 ohms so they could operate well with high-impedance tube amplifiers. In contrast, modern transistor amplifiers can have very low output impedance, enabling lower-impedance headphones. Unfortunately, this means that older audio amplifiers or stereos often produce poor-quality output on some modern, low-impedance headphones. In this case, an external headphone amplifier may be beneficial.
Sensitivity
[edit]Sensitivity is a measure of how effectively an earpiece converts an incoming electrical signal into an audible sound. It thus indicates how loud the headphones are for a given electrical drive level. It can be measured in decibels of sound pressure level per milliwatt (dB (SPL)/mW) or decibels of sound pressure level per volt (dB (SPL) / V).[36] Unfortunately, both definitions are widely used, often interchangeably. As the output voltage (but not power) of a headphone amplifier is essentially constant for most common headphones, dB/mW is often more useful if converted into dB/V using Ohm's law:
Once the sensitivity per volt is known, the maximum volume for a pair of headphones can be easily calculated from the maximum amplifier output voltage. For example, for a headphone with a sensitivity of 100 dB (SPL)/V, an amplifier with an output of 1 root mean square (RMS) voltage produces a maximum volume of 100 dB.
Pairing high-sensitivity headphones with power amplifiers can produce dangerously high volumes and damage headphones. The maximum sound pressure level is a matter of preference, with some sources recommending no higher than 110 to 120 dB. In contrast, the American Occupational Safety and Health Administration recommends an average SPL of no more than 85 dB(A) to avoid long-term hearing loss, while the European Union standard EN 50332-1:2013 recommends that volumes above 85 dB(A) include a warning, with an absolute maximum volume (defined using 40–4,000 Hz noise) of no more than 100 dB to avoid accidental hearing damage.[37] Using this standard, headphones with sensitivities of 90, 100 and 110 dB (SPL)/V should be driven by an amplifier capable of no more than 3.162, 1.0 and 0.3162 RMS volts at maximum volume setting, respectively to reduce the risk of hearing damage.
The sensitivity of headphones is usually between about 80 and 125 dB/mW and usually measured at 1 kHz.[38]
Specifications
[edit]Headphone size can affect the balance between fidelity and portability. Generally, headphone form factors can be divided into four separate categories: circumaural (over-ear), supra-aural (on-ear), earbud and in-ear.
Connectivity
[edit]Wired
[edit]Wired headphones make a direct electrical connection to the source device using a cable, typically connected with a headphone jack.
Wireless
[edit]Modern wireless or cordless earphones have no cord connecting the two earphones to the source device or to each other; they receive audio by means of a wireless technology such as Bluetooth. In historical usage, 'wireless' referred to a connection to a radio receiver, which was known as a wireless.
On some models both audio streams are transmitted to one earphone which forwards one stream to the other earphone. On other models each earphone receives its audio stream directly from the source device. The former arrangement has the advantage of being compatible with legacy systems while the latter arrangement has the advantage of causing less power drain in the earphone that has to forward one audio stream.
Connection between the two earphones also being wireless may be referred to as true wireless stereo (TWS), offering longer battery life and complete transmission on left and right channels, avoiding possible source signal omission if only one is worn. [39]
Ear adaption
[edit]Circumaural
[edit]
Circumaural headphones (sometimes called full size headphones or over-ear headphones) have circular or ellipsoid earpads that encompass the ears. Because these headphones completely surround the ear, circumaural headphones can be designed to fully seal against the head to attenuate external noise. Because of their size, circumaural headphones can be heavy and there are some sets that weigh over 500 grams (1 lb). Ergonomic headband and earpad design is required to reduce discomfort resulting from weight. These are commonly used by drummers in recording.
Supra-aural
[edit]
Supra-aural headphones or on-ear headphones have pads that press against the ears, rather than around them. They were commonly bundled with personal stereos during the 1980s. This type of headphone generally tends to be smaller and lighter than circumaural headphones, resulting in less attenuation of outside noise. Supra-aural headphones can also lead to discomfort due to the pressure on the ear as compared to circumaural headphones that sit around the ear. Comfort may vary due to the earcup material.
Ear-fitting headphones
[edit]Earphones
[edit]Earphones are very small headphones that are fitted directly in the outer ear, facing but not inserted in the ear canal. Earphones are portable and convenient, but many people consider them uncomfortable.[40][failed verification] They provide hardly any acoustic isolation and leave room for ambient noise to seep in; users may turn up the volume dangerously high to compensate, at the risk of causing hearing loss.[40][41] On the other hand, they let the user be better aware of their surroundings. Since the early days of the transistor radio, earphones have commonly been bundled with personal music devices. They are sold at times with foam or rubber pads for comfort. (The use of the term earbuds, which has been around since at least 1984, did not hit its peak until after 2001, with the success of Apple's MP3 player.[42])
In-ear headphones
[edit]
In-ear headphones, also known as in-ear monitors (IEMs) or canalphones, are small headphones with similar portability to earbuds that are inserted in the ear canal itself. IEMs are higher-quality in-ear headphones and are used by audio engineers and musicians as well as audiophiles.
The outer shells of in-ear headphones are made up of a variety of materials, such as plastic, aluminum, ceramic and other metal alloys. Because in-ear headphones engage the ear canal, they can be prone to sliding out, and they block out much environmental noise. Lack of sound from the environment can be a problem when sound is a necessary cue for safety or other reasons, as when walking, driving, or riding near or in vehicular traffic.[43] Some in-ear headphones utilize built-in microphones to allow some outside sound to be heard when desired.[44][45]
Generic or custom-fitting ear canal plugs are made from silicone rubber, elastomer, or foam. Such plugs in lower-end devices may be interchangeable, which increases the risk of them falling off and getting lodged in the ear canal. Custom in-ear headphones use castings of the ear canal to create custom-molded plugs that provide added comfort and noise isolation.[40]
Some wireless earphones include a charging case.
Open- or closed-back
[edit]Both circumaural and supra-aural headphones can be further differentiated by the type of earcups:
- Open-back
- Headphones having the back of the earcups open. This leaks more sound out of the headphone and also lets more ambient sounds into the headphone, but gives a more natural or speaker-like sound, due to including sounds from the environment.
- Semi-open
- They have a design that can be considered as a compromise between open-back headphones and closed-back headphones. Some[who?] believe the term "semi-open" is purely there for marketing purposes. There is no exact definition for the term semi-open headphone. Where the open-back approach has hardly any measure to block sound at the outer side of the diaphragm and the closed-back approach really has a closed chamber at the outer side of the diaphragm, a semi-open headphone can have a chamber to partially block sound while letting some sound through via openings or vents.
- Closed-back
- Closed-back (or sealed) styles have the back of the earcups closed. They usually block some of the ambient noise. Closed-back headphones usually can produce stronger low frequencies than open-back headphones.
Headset
[edit]
A headset is a headphone combined with a microphone. Headsets provide the equivalent functionality of a telephone handset with hands-free operation. Among applications for headsets, besides telephone use, are aviation, theatre or television studio intercom systems, and console or PC gaming. Headsets are made with either a single-earpiece (mono) or a double-earpiece (mono to both ears or stereo). The microphone arm of headsets is either an external microphone type where the microphone is held in front of the user's mouth, or a voicetube type where the microphone is housed in the earpiece and speech reaches it by means of a hollow tube.
Telephone headsets
[edit]
Telephone headsets connect to a fixed-line telephone system. A telephone headset functions by replacing the handset of a telephone. Headsets for standard corded telephones are fitted with a standard 4P4C commonly called an RJ-9 connector. Headsets are also available with 2.5 mm jack sockets for many DECT phones and other applications. Cordless bluetooth headsets are available, and often used with mobile telephones. Headsets are widely used for telephone-intensive jobs, in particular by call centre workers. They are also used by anyone wishing to hold telephone conversations with both hands free.
For older models of telephones, the headset microphone impedance is different from that of the original handset, requiring a telephone amplifier for the telephone headset. A telephone amplifier provides basic pin-alignment similar to a telephone headset adaptor, but it also offers sound amplification for the microphone as well as the loudspeakers. Most models of telephone amplifiers offer volume control for loudspeaker as well as microphone, mute function and switching between headset and handset. Telephone amplifiers are powered by batteries or AC adaptors.
Communication headsets
[edit]
Communication headsets are used for two-way communication and typically consist of a headphone and attached microphone. Such headsets are used in a variety of professions as aviation, military, sports, music, and many service-oriented sectors. They come in all shapes and sizes, depending on use, required noise attenuation, and fidelity of communication needed.
Ambient noise reduction
[edit]Unwanted sound from the environment can be reduced by excluding sound from the ear by passive noise isolation, or, often in conjunction with isolation, by active noise cancellation.

Passive noise isolation is essentially using the body of the earphone, either over or in the ear, as a passive earplug that simply blocks out sound. The headphone types that provide most attenuation are in-ear canal headphones and closed-back headphones, both circumaural and supra aural. Open-back and earbud headphones provide some passive noise isolation, but much less than the others. Typical closed-back headphones block 8 to 12 dB, and in-ears anywhere from 10 to 15 dB. Some models have been specifically designed for drummers to facilitate the drummer monitoring the recorded sound while reducing sound directly from the drums as much as possible. Such headphones claim to reduce ambient noise by around 25 dB.
Active noise-cancelling headphones use a microphone, amplifier, and speaker to pick up, amplify, and play ambient noise in phase-reversed form; this to some extent cancels out unwanted noise from the environment without affecting the desired sound source, which is not picked up and reversed by the microphone. They require a power source, usually a battery, to drive their circuitry. Active noise cancelling headphones can attenuate ambient noise by 20 dB or more, but the active circuitry is mainly effective on constant sounds and at lower frequencies, rather than sharp sounds and voices. Some noise cancelling headphones are designed mainly to reduce low-frequency engine and travel noise in aircraft, trains, and automobiles, and are less effective in environments with other types of noise.
Transducer technology
[edit]Headphones use various types of transducer to convert electrical signals to sound.
Moving-coil
[edit]
The moving coil driver, more commonly referred to as a "dynamic" driver is the most common type used in headphones. It consists of a stationary magnet element affixed to the frame of the headphone, which sets up a static magnetic field. The magnet in headphones is typically composed of ferrite or neodymium. A voice coil, a light coil of wire, is suspended in the magnetic field of the magnet, attached to a diaphragm, typically fabricated from lightweight, high-stiffness-to-mass-ratio cellulose, polymer, carbon material, paper or the like. When the varying current of an audio signal is passed through the coil, it creates a varying magnetic field that reacts against the static magnetic field, exerting a varying force on the coil causing it and the attached diaphragm to vibrate. The vibrating diaphragm pushes on the air to produce sound waves.
Electrostatic
[edit]
Electrostatic drivers consist of a thin, electrically charged diaphragm, typically a coated PET film membrane, suspended between two perforated metal plates (electrodes). The electrical sound signal is applied to the electrodes creating an electrical field; depending on the polarity of this field, the diaphragm is drawn towards one of the plates. Air is forced through the perforations; combined with a continuously changing electrical signal driving the membrane, a sound wave is generated. Electrostatic headphones are usually more expensive than moving-coil ones, and are comparatively uncommon. In addition, a special amplifier is required to amplify the signal to deflect the membrane, which often requires electrical potentials in the range of 100 to 1,000 volts.
Due to the extremely thin and light diaphragm membrane, often only a few micrometers thick, and the complete absence of moving metalwork, the frequency response of electrostatic headphones usually extends well above the audible limit of approximately 20 kHz. The high-frequency response means that the low-midband distortion level is maintained to the top of the audible frequency band, which is generally not the case with moving coil drivers. Also, the frequency response peakiness regularly seen in the high-frequency region with moving coil drivers is absent. Well-designed electrostatic headphones can produce significantly better sound quality than other types.[citation needed]
Electrostatic headphones require a voltage source generating 100 V to over 1 kV, and are on the user's head. Since the invention of insulators, there is no actual danger. They do not need to deliver significant electric current, which further limits the electrical hazard to the wearer in case of fault.
Electret
[edit]An electret driver functions along the same electromechanical means as an electrostatic driver. However, the electret driver has a permanent charge built into it, whereas electrostatics have the charge applied to the driver by an external generator. Electret and electrostatic headphones are relatively uncommon. Original electrets were also typically cheaper and lower in technical capability and fidelity than electrostatics. Patent applications from 2009 to 2013 have been approved that show by using different materials, i.e. a "Fluorinated cyclic olefin electret film", Frequency response chart readings can reach 50 kHz at 100 db. When these new improved electrets are combined with a traditional dome headphone driver, headphones can be produced that are recognised by the Japan Audio Society as worthy of joining the Hi Res Audio program. US patents 8,559,660 B2. 7,732,547 B2.7,879,446 B2.7,498,699 B2.
Planar magnetic
[edit]Planar magnetic (also known as orthodynamic) headphones use similar technology to electrostatic headphones, with some fundamental differences. They operate similarly to planar magnetic loudspeakers.
A planar magnetic driver consists of a relatively large membrane that contains an embedded wire pattern. This membrane is suspended between two sets of permanent, oppositely aligned, magnets. A current passed through the wires embedded in the membrane produces a magnetic field that reacts with the field of the permanent magnets to induce movement in the membrane, which produces sound.
Balanced armature
[edit]A balanced armature is a sound transducer design primarily intended to increase the electrical efficiency of the element by eliminating the stress on the diaphragm characteristic of many other magnetic transducer systems. As shown schematically in the left diagram, it consists of a moving magnetic armature that is pivoted so it can move in the field of the permanent magnet. When precisely centered in the magnetic field there is no net force on the armature, hence the term 'balanced'. As illustrated in the right diagram, when there is electric current through the coil, it magnetizes the armature one way or the other, causing it to rotate slightly one way or the other about the pivot thus moving the diaphragm to make sound.

The design is not mechanically stable; a slight imbalance makes the armature stick to one pole of the magnet. A fairly stiff restoring force is required to hold the armature in the 'balance' position. Although this reduces its efficiency, this design can still produce more sound from less power than any other.[clarification needed] Popularized in the 1920s as Baldwin Mica Diaphragm radio headphones, balanced armature transducers were refined during World War II for use in military sound powered telephones. Some of these achieved astonishing electro-acoustic conversion efficiencies, in the range of 20% to 40%, for narrow bandwidth voice signals.
Today they are typically used only in in-ear headphones and hearing aids, where their high efficiency and diminutive size is a major advantage.[47] They generally are limited at the extremes of the hearing spectrum (e.g. below 20 Hz and above 16 kHz) and require a better seal than other types of drivers to deliver their full potential. Higher-end models may employ multiple armature drivers, dividing the frequency ranges between them using a passive crossover network. A few combine an armature driver with a small moving-coil driver for increased bass output.
The earliest loudspeakers for radio receivers used balanced armature drivers for their cones.[48]
Thermoacoustic technology
[edit]The thermoacoustic effect generates sound from the audio frequency Joule heating of the conductor, an effect that is not magnetic and does not vibrate the speaker. In 2013 a carbon nanotube thin-yarn earphone based on the thermoacoustic mechanism was demonstrated by a research group in Tsinghua University.[49] The as-produced CNT thin yarn earphone has a working element called CNT thin yarn thermoacoustic chip. Such a chip is composed of a layer of CNT thin yarn array supported by the silicon wafer, and periodic grooves with certain depth are made on the wafer by micro-fabrication methods to suppress the heat leakage from the CNT yarn to the substrate.[citation needed]
Other transducer technologies
[edit]Transducer technologies employed much less commonly for headphones include the Heil Air Motion Transformer (AMT); Piezoelectric film; Ribbon planar magnetic; Magnetostriction and Plasma or Ionic. The first Heil AMT headphone was marketed by ESS Laboratories and was essentially an ESS AMT tweeter from one of the company's speakers being driven at full range. Since the turn of the century, only Precide of Switzerland have manufactured an AMT headphone. Piezoelectric film headphones were first developed by Pioneer, their two models used a flat sheet of film that limited the maximum volume of air movement. Currently, TakeT produces a piezoelectric film headphone shaped similarly to an AMT transducer but, which like the Precide driver, has a variation in the size of transducer folds over the diaphragm. It additionally incorporates a two way design by its inclusion of a dedicated tweeter/supertweeter panel. The folded shape of a diaphragm allows a transducer with a larger surface area to fit within smaller space constraints. This increases the total volume of air that can be moved on each excursion of the transducer given that radiating area.
Magnetostriction headphones, sometimes sold under the label Bonephones, work by vibrating against the side of head, transmitting sound via bone conduction. This is particularly helpful in situations where the ears must be unobstructed, or for people who are deaf for reasons that do not affect the nervous apparatus of hearing. Magnetostriction headphones though, are limited in their fidelity compared to conventional headphones that rely on the normal workings of the ear. Additionally, in the mid-1980s, a French company called Audio Reference tried to market the Plasmasonic plasma headphone invented by Henri Bondar.[50][51] There are no known functioning examples left. Due to the small volume of air in a headphone, the plasma or ionic transducer can become a full range driver although the high temperatures and voltages needed makes them very rare.
Benefits and limitations
[edit]

Headphones can prevent other people from hearing the sound, either for privacy or to prevent disturbing others, as in listening in a public library. They can also provide a level of sound fidelity greater than loudspeakers of similar cost. Part of their ability to do so comes from the lack of any need to perform room correction treatments with headphones. High-quality headphones can have an extremely flat low-frequency response down to 20 Hz within 3 dB. While a loudspeaker must use a relatively large (often 15" or 18") speaker driver to reproduce low frequencies, headphones can accurately reproduce bass and sub-bass frequencies with speaker drivers only 40-50 millimeters wide (or much smaller, as is the case with in-ear monitor headphones). Headphones' impressive low-frequency performance is possible because they are so much closer to the ear that they only need to move relatively small volumes of air.
Marketed claims such as 'frequency response 4 Hz to 20 kHz' are usually overstatements; the product's response at frequencies lower than 20 Hz is typically very small.[52] Headphones are also useful for video games that use 3D positional audio processing algorithms, as they allow players to better judge the position of an off-screen sound source (such as the footsteps of an opponent or their gunfire).
Although modern headphones have been particularly widely sold and used for listening to stereo recordings since the release of the Walkman, there is subjective debate regarding the nature of their reproduction of stereo sound. Stereo recordings represent the position of horizontal depth cues (stereo separation) via volume and phase differences of the sound in question between the two channels. When the sounds from two speakers mix, they create the phase difference the brain uses to locate direction. Through most headphones, because the right and left channels do not combine in this manner, the illusion of the phantom center can be perceived as lost. Hard panned sounds are also heard only in one ear rather than from one side.
Binaural recordings use a different microphone technique to encode direction directly as phase, with very little amplitude difference below 2 kHz, often using a dummy head. They can produce a surprisingly lifelike spatial impression through headphones. Commercial recordings almost always use stereo recording, rather than binaural, because loudspeaker listening is more common than headphone listening.
It is possible to change the spatial effects of stereo sound on headphones, to better approximate the presentation of speaker reproduction, by using frequency-dependent cross-feed between the channels.
Headsets can have ergonomic benefits over traditional telephone handsets. They allow call center agents to maintain better posture without needing to hand-hold a handset or tilt their head sideways to cradle it.[53]
Health and safety
[edit]Dangers and risks
[edit]
Using headphones at a sufficiently high volume level may cause temporary or permanent hearing impairment or deafness. The headphone volume often has to compete with the background noise, especially in loud places such as subway stations, aircraft, and large crowds. Extended periods of exposure to high sound pressure levels created by headphones at high volume settings may be damaging to hearing;[54][55] Nearly 50% of teenagers and young adults (12 to 35 years old) in middle and high income countries listen to unsafe levels of sound on their personal audio devices and smartphones.[56] However, one hearing expert found in 2012 (before the worldwide adoption of smartphones as the main personal listening devices) that "fewer than 5% of users select volume levels and listen frequently enough to risk hearing loss."[57] The International Telecommunication Union recently published "Guidelines for safe listening devices/systems" recommended that sound exposure not exceed 80 decibels, A-weighted dB(A) for a maximum of 40 hours per week.[58] The European Union have also set a similar limit for users of personal listening devices (80 dB(A) for no more than 40 hours per week) and for each additional increase of 3-dB in sound exposure, the duration should be cut in half (83 dB(A) for no more than 20 hours, 86 dB(A) for 10 hours per week, 89 dB(A) for 5 hours per week and so on. Most major manufactures of smartphones now include some safety or volume limiting features and warning messaging in their devices.[59][60] though such practices have received mixed response from some segments of the buying who favor the personal choice of setting their own volume levels.
The usual way of limiting sound volume on devices driving headphones is by limiting output power. This has the additional undesirable effect of being dependent of the efficiency of the headphones; a device producing the maximum allowed power may not produce adequate volume when paired with low-efficiency, high-impedance equipment, while the same amount of power can reach dangerous levels with very efficient earphones.
Some studies have found that people are more likely to raise volumes to unsafe levels while performing strenuous exercise.[61] A Finnish study[62] recommended that exercisers should set their headphone volumes to half of their normal loudness and only use them for half an hour.
Other than hearing risk, there is a general danger that listening to loud music in headphones can distract the listener and lead to injury and accidents.[63][64] Noise-cancelling headphones add extra risk. Several countries and states have made it illegal to wear headphones while driving or cycling.[43]
There have also been numerous reports of contact dermatitis due to exposure to in-ear headphones such as Apple AirPods.[65][66] The contact dermatitis would be caused by in-ear headphones that contain gold, rubber, dyes, acrylates, or methacrylates.[65] However, there have been no studies done to prove that exposure to in-ear headphones will cause contact dermatitis, rather that there is a correlation between in-ear headphone use and contact dermatitis cases.[65]
Occupational health and safety
[edit]Hearing risk from headphones' use also applies to workers who must wear electronic or communication headsets as part of their daily job (i.e., pilots, call center and dispatch operators, sound engineers , firefighters, etc.) and hearing damage depends on the exposure time. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends sound exposure not exceed 85 dB(A) over 8 hour work day as a time-weighted average.[67] NIOSH uses the 3-dB exchange rate often referred to as "time-intensity tradeoff" which means if sound exposure level is increased by 3 decibels, the duration of exposure should be cut in half. NIOSH published several documents targeted at protecting the hearing of workers who must wear communication headsets such as call center operators,[68] firefighters,[69] and musicians and sound engineers.[70][71]
See also
[edit]- Bone conduction
- Digital audio player
- Earmuffs
- Headphone amplifier
- In-ear monitor
- Loudspeaker
- Noise-cancelling headphones
References
[edit]- ^ a b "earphone". Archived from the original on 19 January 2014. Retrieved 4 January 2014.
- ^ Stanley R. Alten Audio Basics Cengage 2011 ISBN 0-495-91356-1 page 63
- ^ "Headphones : The Ultimate buying guide - Hi-fidelity headphones". StereoCompare. Archived from the original on 2016-03-07. Retrieved 2016-03-03.
- ^ "The Ultimate Headphones Buying Guide - Audio Inspects". 2022-06-20. Retrieved 2022-07-15.
- ^ Sullivan, Mark (7 January 2016). "It's True: Apple Will Drop Headphone Jack To Make The iPhone 7 Slimmer, Says Source". Fast Company. Archived from the original on 2016-08-29.
- ^ "Rewind: How the Walkman changed the world..." independent. 15 July 2009.
- ^ Prescott, George Bartlett (1884). Bell's Electric Speaking Telephone: Its Invention, Construction, Application, Modification, and History. D. Appleton. p. 137.
The transmitter is placed on an upright rod at his right and the receiver is held constantly at his ear by means of a steel band passed over the head which band serves also as the magnet of the telephone He is therefore always in readiness to receive an order without the necessity of a preliminary call or signal and both his hands are left free to fill the orders. [Also see Figure 180]
- ^ "The Telephone Problem in the World's Largest Metropolitan Area: A Summary of Past and Present". Bell Telephone Magazine. XIII. Prelinger Library. American Telephone and Telegraph Company: 248. October 1934.
Upper right image: A New York City central office in the '80s, showing "beehive" as well as early desk type switchboards, and both young women and boy operators [Note image of telephone operator's with head-mounted telephone receivers]
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Herbert, Thomas Ernest (1898). The Telephone System of the British Post Office: A Practical Handbook. Page & Pratt. p. 85.
Figure 73
- ^ "Some new Bell type switchboard accessories". Electrical Engineering and Telephone Magazine. Vol. XII. November 1898. p. 194.
Figure 1
- ^ "Polk's Busy Test For Telephone Switchboards". Illustrated Electrical Review: A Journal of Scientific and Electrical Progress. 25. Electrical Review Publishing Company: 251, 254. November 21, 1894.
Referring to the illustrations on page 251, A is the switchboard, B is the inclined shelf usually employed in upright switchboards and C is the headphone.
- ^ "Behind the scenes at "Central"". The Book Lover's Magazine. Vol. II. Library Publishing Company. October 1903. pp. 390–401.
For the first week she does nothing but attach her headphone to an experienced operator's position and listen. [pp. 401]
- ^ "Head Clamp Receiver (c.1883)". Collection of historical scientific instruments -- Harvard University. Retrieved 2023-05-06.
- ^ a b "A Partial History of Headphones". Smithsonian Magazine. Retrieved 2020-12-27.
- ^ U.S. Patent No. 454,138 for "improvements in telephone-receivers...which shall be light enough to be carried while in use on the head of the operator."
- ^ Preece, Sir William Henry; Stubbs, Arthur James (1893). A Manual of Telephony. Whittaker and Company. pp. 55–58.
- ^ a b Collins, Archie Frederick (December 1902). "Review of wireless telegraph engineering practice". Telephony. Vol. 4. Telephone Publishing Corporation. pp. 279–288.
- ^ "The De Forest Wireless Telegraph Station at Coney Island". Electrical Age. Vol. 29. Electrical Age Publishing Company. July 1902. p. 181.
- ^ Bullard, William Hannum Grubb (1908). Naval Electricians' Text Book. United States Naval Institute. p. 927.
Listening in --. Keep the head phones on the head and at end of every sentence throw up listening key with fingers or thumb of right hand to assure yourself that the other party hears you clearly and answers you
- ^ McCaskey, E. L. (May 22, 1909). "Correspondence". Modern Electrics. Vol. II. Modern electrics publication. p. 102.
My headphones are of the single pole type wound to the resistance of 3,000 ohms.
- ^ a b Electrical Construction and Maintenance. McGraw-Hill Publishing Company. April 1909. p. 10.
- ^ Singer, Merril (1979). "Nathaniel Baldwin, Utah inventor and patron of the fundamentalist movement". Utah Historical Quarterly. 47 (1): 42–53. doi:10.2307/45060660. JSTOR 45060660. S2CID 254434880.
- ^ Howeth, Linwood S. (1963). History of Communications Electronics in the United States Navy. U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 148–149.
- ^ "Great Falls Tribune 03 Jan 1930, page 7". Newspapers.com. Retrieved 2023-04-30.
- ^ Heffernan, Virginia (2011-01-07). "Against Headphones". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2023-05-06.
- ^ a b Smith, Caspar (30 October 2011). "Now hear this: the history of headphones". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 13 September 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ "Founded 1958 - World's First SP/3 Stereophone". koss.com. Archived from the original on 13 September 2017. Retrieved 13 September 2017.
- ^ "Sony history 1960s". Sony official website. Archived from the original on 2016-02-05.
- ^ Description of 3.5mm earphone jack in described model:
"Vintage Sony 1960'S EFM-117J Radio". Retrieved 2016-01-25. - ^ Arce, Nicole (2020-07-22). "How To Use Two Or More Headphones On PC or Mac (Wired/Bluetooth) - Headphonesty". Retrieved 29 May 2021.
- ^ Hearing conservation manual. Hutchison, Thomas L., Schulz, Theresa Y., Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation. (Fifth ed.). Milwaukee, WI. 2014. ISBN 978-0-9863038-0-7. OCLC 940449158.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b c Handbook of clinical audiology. Katz, Jack, Chasin, Marshall, English, Kristina M., 1951-, Hood, Linda J., Tillery, Kim L. (Seventh ed.). Philadelphia. 2015. ISBN 978-1-4511-9163-9. OCLC 877024342.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ "ANSI/ASA S3.6-2018 - Specification for Audiometers". webstore.ansi.org. Retrieved 2020-11-13.
- ^ "ISO 389-2:1994". ISO. Retrieved 2020-11-13.
- ^ Siau, John. "The "0-Ohm" Headphone Amplifier" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 February 2013. Retrieved 26 June 2012.
- ^ Bohn, Dennis. "Understanding Headphone Power Requirements". HeadWize. Northwestern University. Archived from the original on 2011-06-08.
- ^ "BS EN 50332 tests for headphones and earphones with portable music players". ISVR Consulting. 2 August 2018. Archived from the original on 2018-08-21.
- ^ "Understanding Earphone/Headphone Specifications". Shure Customer Help. Shure. Archived from the original on 2016-06-18.
- ^ Telink Staff (19 Aug 2020). "An Introduction to True Wireless Stereo (TWS) Technology". Telink Semiconductor (Press release). Archived from the original on 2024-01-18.
- ^ a b c Ha, Peter (26 April 2010). "Custom-Made Headphones: Listen Up Before It's Too Late". Time. Archived from the original on 17 August 2013. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ Fligor, Brian J.; Cox, L. Clarke (December 2004). "Output Levels of Commercially Available Portable Compact Disc Players and the Potential Risk to Hearing". Ear and Hearing. 25 (6): 513–27. doi:10.1097/00003446-200412000-00001. PMID 15604913. S2CID 11043107. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ Engber, Daniel (16 May 2014). "Who Made That Earbud?". The New York Times Magazine. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02.
- ^ a b "Headphones as a Driving Distraction" (PDF). The Royal Society for the Prevention of Accidents. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 September 2017. Retrieved 14 September 2017.
- ^ "Use Ambient sound on your Samsung earbuds". Samsung Electronics America. Retrieved 2021-08-13.
- ^ "WF-1000XM3 | Help Guide | Listening to ambient sound during music playback (Ambient Sound Mode)". helpguide.sony.net. Retrieved 2021-08-13.
- ^ "Lightspeed Aviation 30 3G Discontinued Aviation Headset". lightspeedaviation.com. Retrieved 26 Dec 2020.
- ^ Hertsens, Tyll (2014-12-15). "How Balanced Armature Receivers/Drivers Work". InnerFidelity. Archived from the original on 2015-09-14.
- ^ Joel, Amos E. (1975). A History of Engineering and Science in the Bell System: The early years (1875-1925). The Laboratories. ISBN 9780608080666.
- ^ Yang Wei; Xiaoyang Lin; Kaili Jiang; Peng Liu; Qunqing Li; Shoushan Fan (2013). "Thermoacoustic Chips with Carbon Nanotube Thin Yarn Arrays". Nano Letters. 13 (10): 4795–801. Bibcode:2013NanoL..13.4795W. doi:10.1021/nl402408j. PMID 24041369.
- ^ "Plasmasonic". La Nouvelle Revue Du Son. FR. March 1984. p. 100.
- ^ US 4460809A, Henri Bondar, "Process and device for converting a periodic LF electric voltage into sound waves"
- ^ "How to buy headphones". CNET. Archived from the original on 2011-08-20.
Even the flimsiest, cheap headphones routinely boast extremely low bass-response performance—15 or 20Hz—but almost always sound lightweight and bright.
- ^ United States Department of Labor. Occupational Safety & Health Administration. Computer Workstation. Checklist. Archived 2009-02-02 at the Wayback Machine Accessed February 2, 2009.
- ^ "Causes of Hearing Loss in Adults". asha.org. Archived from the original on 13 December 2010. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ "Noise-Induced Hearing Loss". nih.gov. Archived from the original on 9 May 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ World Health Organization (15 Mar 2018). "1.1 billion people at risk of hearing loss". Archived from the original on February 27, 2015. Retrieved 2 Feb 2019.
- ^ William W. Clark. "Five Myths in Assessing the Effects of Noise on Hearing". AudiologyOnline. Archived from the original on 24 September 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ "H.870 : Guidelines for safe listening devices/systems". www.itu.int. Retrieved 2019-02-28.
- ^ "Sound and Hearing". Apple. Retrieved 2019-02-28.
- ^ "Limit Media Volume". Samsung Electronics America. Retrieved 2019-02-28.
- ^ "Can Loud Noise during Exercise Damage my Hearing?". Healthy Hearing. Item 4. Archived from the original on 9 November 2014. Retrieved 8 November 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Airo, Erkko; J. Pekkarinen; P. Olkinuora. "Listening to music with earphones: an assessment of noise exposure," Acustica–Acta Acustica, pp. 82, 885–894. (1996)
- ^ Greenfield, Paige (25 June 2011). "Deaf to Danger: The Perils of Earbuds". ABC News. Archived from the original on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ^ Lichenstein, R; Smith, DC; Ambrose, JL; Moody, LA (October 2012). "Headphone use and pedestrian injury and death in the United States: 2004-2011". Injury Prevention. 18 (5): 287–90. doi:10.1136/injuryprev-2011-040161. PMID 22248915. S2CID 25177965.
- ^ a b c Hayakawa, Michitaro; Suzuki, Chihiro; Zhu, Yingyao; Anzai, Hidemi (April 2022). "Allergic contact dermatitis to gold in the parts of in-ear headphones". Contact Dermatitis. 86 (4): 328–330. doi:10.1111/cod.14036. ISSN 0105-1873. PMID 34978717. S2CID 245651803.
- ^ Chan, Justin; Rabi, Sina; Adler, Brandon L. (November 2021). "Allergic Contact Dermatitis to (Meth)Acrylates in Apple AirPods Headphones". Dermatitis. 32 (6): e111–e112. doi:10.1097/DER.0000000000000735. ISSN 2162-5220. PMID 34807535. S2CID 233923350.
- ^ "Occupational noise exposure; criteria for a recommended standard". CDC. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. June 1998. doi:10.26616/NIOSHPUB98126.
- ^ "Reducing Noise Hazards for Call & Dispatch Center Operators". CDC. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. September 2011. doi:10.26616/NIOSHPUB2011210.
- ^ "Promoting Hearing Health among Firefighters". CDC. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. May 2013. doi:10.26616/NIOSHPUB2013142.
- ^ "Reducing the risk of hearing disorders among musicians". CDC. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. June 2015. doi:10.26616/NIOSHPUB2015184.
- ^ McGinnity, Siobhan; Beach, Elizabeth Francis; Cowan, Robert S. C.; Mulder, Johannes (2020-10-22). "The hearing health of live-music sound engineers". Archives of Environmental & Occupational Health. 76 (6): 301–312. Bibcode:2021ArEOH..76..301M. doi:10.1080/19338244.2020.1828241. ISSN 2154-4700. PMID 33089760. S2CID 224821849.
External links
[edit] Media related to Headphones at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Headphones at Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition of earphone at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of earphone at Wiktionary- Earpad